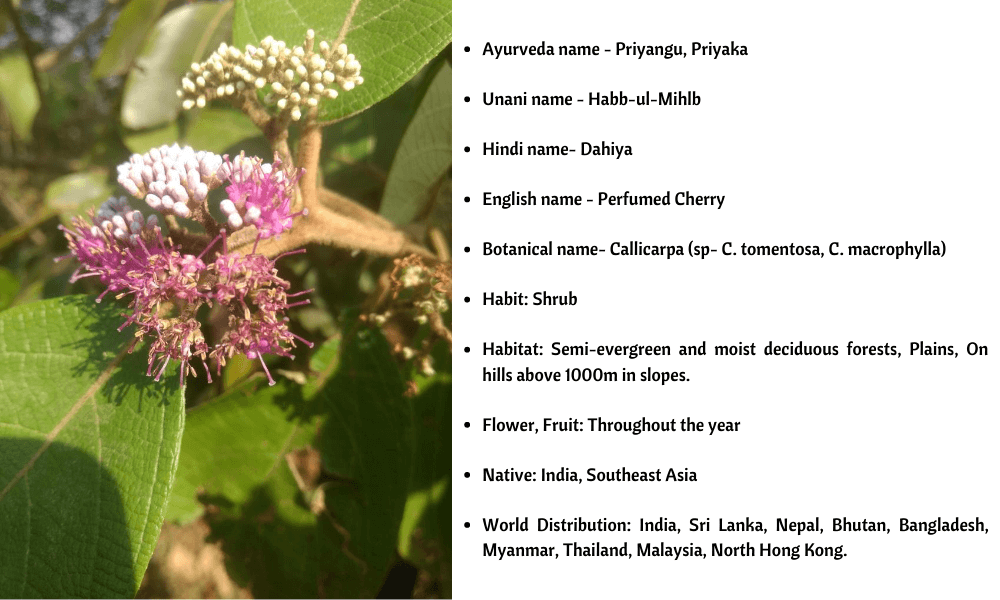
Nature has bestowed us with abundant medicinal herbs that help to treat several illnesses. Our ancestors have recognised such herb’s abilities and used them in medicinal formulations. Genus Callicarpa is one such herb with remarkable medicinal properties. It has long been used in traditional medicine systems, including the TCM and Ayurveda and is found in several natural products and traditional medicines. This article explores the herb’s therapeutic benefits and also the little available scientific research. In addition, you will learn about the origin and traditional uses of Callicarpa.
Genus Callicarpa comprises 40 or more species; many are reported with different beneficial properties. Many species, including Callicarpa tomentosa, have ethnomedicinal uses, such as the treatment of hepatitis, rheumatism, headache, fever, indigestion, and others.
Scientific Research
Some medicinal herbs, such as moringa and turmeric, are extensively studied and evaluated for their health benefits. However, on the other hand, many other herbs with potential medical uses need more scientific research. One such is Callicarpa, with limited research, and we hope more studies occur and the herb becomes mainstream in treatments.
Extracts from about fourteen species in this genus have been evaluated for various medicinal properties, including antibacterial, antifungal, anti-insect growth, cytotoxic, and phytotoxic activity. In addition to amino acids, simple carbohydrates and lipids, benzenoids, flavonoids, numerous diterpenes, phytosterols, sesquiterpenes, phenylpropanoids, and triterpenes occur in or isolated from the genus Callicarpa.
Recommended Reads
- Herbs in Traditional Chinese Medicine – An Overview
- Kashayam-An Effective Home Remedy For Common Cold
- The Health Benefits Of Amla – Proven By Study
- Bacopa Monnieri (Brahmi) – The Herb With Remarkable Medicinal Benefits
Traditional Uses
In Ayurveda literature, Priyangu is described as cooling, refrigerant, deodorant, and antipyretic.
The benefits of Callicarpa tomentosa include toning up the digestive system, checking excessive perspiration and helping to disinfect intestines. Other uses include controlling diarrhoea and reducing the burning sensation during fever.
Specific Uses Include
- Leaves, when applied on joints, relieve rheumatic pain
- Oil from the root is aromatic and hence are natural mosquito repellants
- Juice extract from the roots of Callicarpa tomentosa and resin from the bark of Terminalia elliptica (common name – asna, saj or Indian laurel) cure stomach ache
- Study shows that Callicarpa americana (common name- American beautyberry) root treats skin cancer
- Further, the bark of Callicarpa rubella treats tumours of the large intestine
- Callicarpa leaves have antiseptic properties; the paste of leaves, when topically applied, treats boils and eczema
- In addition, applying leaf paste with coconut oil locally three times a day for five days will heal fresh wounds
- Callicarpa flowers treat nervous system disorders and haemorrhages
Wrapping up,
The family of callicarpa has long been used in many traditional medicine systems, including the TCM and Ayurveda. In addition, much to the delight of holistic wellness enthusiasts, the uses are being studied by researchers. If you intend to use this medicinal herb to treat certain illnesses, you may approach a wellness practitioner who can help you.
Edited by love4wellness
References:
- “Journal of Medicinal Plants Research – Ethnobotanically Important Trees and Their Uses by Kattunaikka Tribe in Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary, Kerala, India.” Academic Journals, 18 Feb. 2011, academicjournals.org/journal/JMPR/article-abstract/BD0149C26179.
- “Biologically Active Natural Products of the Genus Callicarpa: Ingenta Connect.” Home: Ingenta Connect, www.ingentaconnect.com/content/ben/cbc/2008/00000004/00000001/art00003.
- “Ethnomedicinal Plants to Cure Skin Diseases—An Account of the Traditional Knowledge in the Coastal Parts of Central Western Ghats, Karnataka, India.” ScienceDirect.com | Science, Health and Medical Journals, Full Text Articles and Books, www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0378874113007885.
- “Lesser Known Ethnomedicinal Plants of the Ayyakarkoil Forest Province of Southwestern Ghats, Tamil Nadu, India—Part I.” Taylor & Francis, 11 Oct. 2008, www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1300/J044v10n04_10.
- “NOPR: Hundred Common Forest Medicinal Plants of Karnataka in Primary Healthcare.” NOPR, nopr.niscair.res.in/handle/123456789/7160.
- Sankara Rao, K., Raja K Swamy, Deepak Kumar, Arun Singh R. and K. Gopalakrishna Bhat (2019). Flora of Peninsular India. http://peninsula.ces.iisc.ac.in/plants.php?name=Callicarpa tomentosa