Diabetes is one of the prevalent diseases of this century, with about 10% of the global population living with it. Let us not be sober, though. The good news is that the awareness about the disease and ways to manage it is also soaring quite high. Studies show that including 15-20% of a meal with protein reduces blood sugar spikes and control blood sugar. This article explains why protein can hugely help manage blood sugar spikes in people with diabetes.
What happens in your body after you eat your meal?
When you eat, the carbs in your food get converted into glucose; sensing this, the body secretes the hormone insulin, enabling the cells to absorb glucose as energy.
When your body does not produce enough insulin or does not use insulin properly, the cells do not absorb glucose properly, and the glucose stays in your blood for a long time.
As you may know, your blood should only contain a nominal amount of sugar. More than that can cause immediate symptoms such as fatigue, irritation, frequent urination, increased thirst and hunger, etc. and risks for heart disease, hypertension, kidney disease, etc., in the long term.
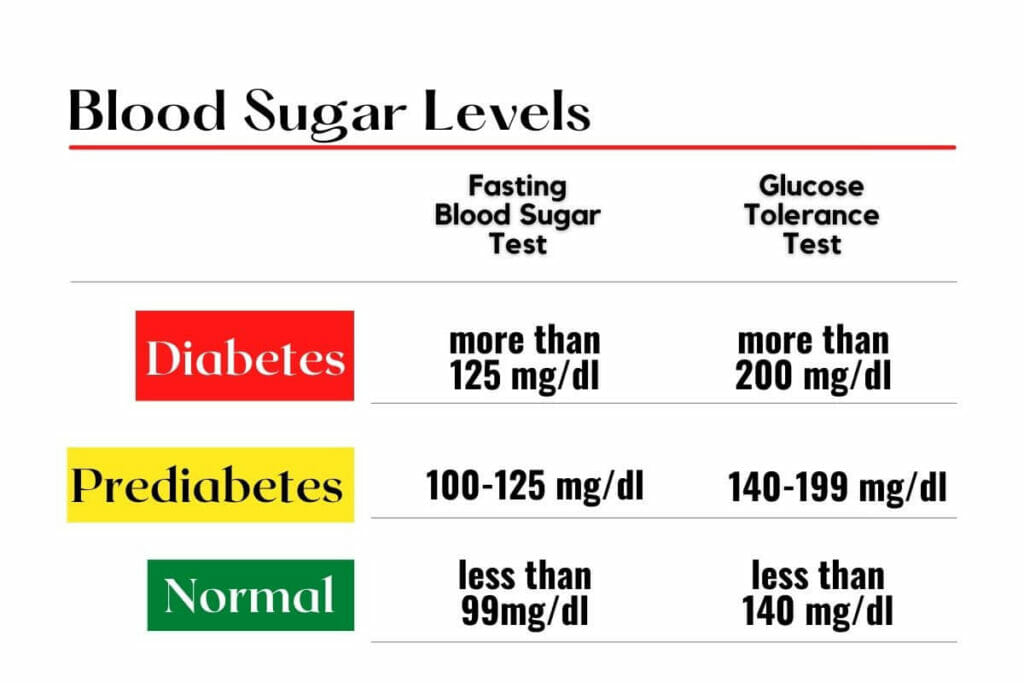
Are you a person with diabetes or prediabetes? Apart from medications, you can try several ways to have your blood sugar at a near-optimal level and prevent blood sugar spikes after a meal.
One of them is including protein in every meal.
Why does protein improve blood sugar control in people with diabetes?
Research studies show that including protein in every meal improves blood sugar control, reducing the blood sugar spikes postprandially (after consuming food).
Let us be clear. The diet we are talking about is not a low-carb, high protein and high-fat diets, such as Atkin’s or Keto. Instead, this is about your usual diet, but with a conscious addition of protein.
For example, if you take bread with butter and jam. Add a boiled egg or a cup of cooked lentils to add protein to your meal. As simple as that.
Naturally, when more protein is added, you tend to take less bread, reducing carbohydrates.
Also, your body digests protein slowly, compared to carbohydrates. Hence, the immediate blood sugar rise will be due to carbs, which will now be considerably low because you took fewer carbohydrates. So, your blood sugar spikes are less likely when you take a significant amount of protein in your meal.
In addition, protein makes you feel fuller for a long time; hence your hunger pangs become less frequent.
Here is an infographic showing six easy ways to include protein in your meal.
When will this not work?
So, yes, including protein in every meal helps improve blood sugar control.
However, you need to know the following:
- Protein has an insignificant effect on blood glucose only when the insulin is adequate.
- In case of insulin deficiency, protein intake also hastens glucogenesis and results in elevated blood sugar levels.
Here is a detailed explanation of why blood sugar will still spike despite including significant protein in your meal.
Suppose you have diabetes and are on medications. The medications may help to stimulate the pancreas and release more insulin. Thereby, the body gets adequate insulin. Or, you may take insulin injections to compensate for your body’s deficiency in insulin production.
Now, if you do not take medications, your insulin levels needed for glycolysis (where your blood glucose is sent to the cells as energy) may not be adequate.
In such a case, protein will also be processed into energy (gluconeogenesis), increasing your blood sugar and causing spikes after your meal.
So, protein in your meal will help control blood sugar only when your insulin levels are adequate.
Hence, you should not refrain from taking diabetic medications, thinking adding more protein will not increase blood sugar.
On the other hand, if your doctor has not yet put you on diabetic medications, but your blood sugar levels rise a bit higher than normal, adding protein to every meal will definitely help.
So, if you are a non-diabetic person or take adequate insulin, taking protein in every meal is a wonderful thing to do.
To conclude,
Studies show that including about 20% protein in every meal will help control blood sugar spikes. This is particularly helpful in people with diabetes who are likely to suffer from blood sugar spikes if not careful in their food intake.
Images: canva.com